Blended Learning mit Jupyter Notebooks
Autor/innen
Dateien
Abstract
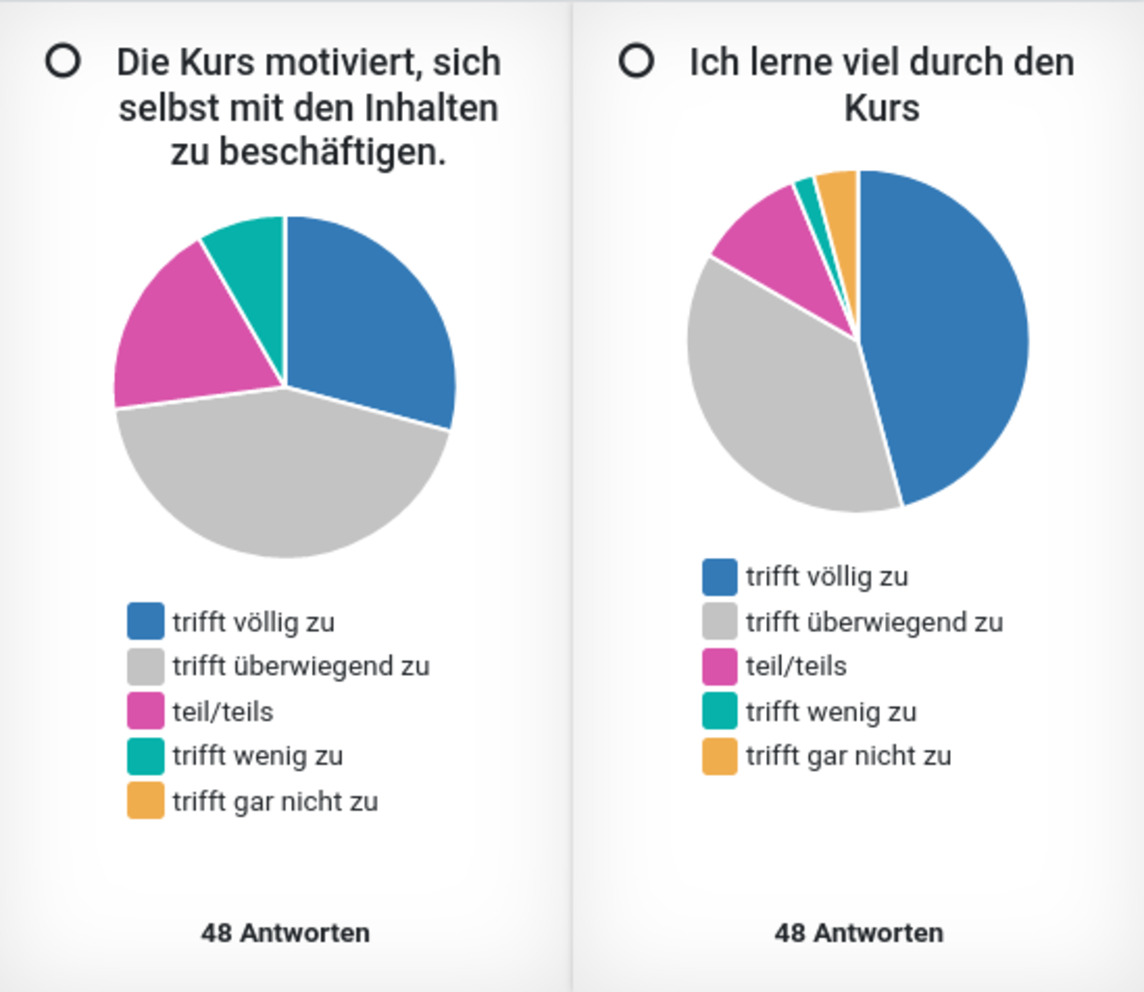
Seit 2021 findet jeweils in der vorlesungsfreien Zeit im Frühjahr der fakultative Blockkurs „Python in der Physik“ als Blended Learning Programmierkurs mit Wissensvermittlung im Inverted Classroom basierend auf Jupyter Notebooks mit interaktiven Elementen sowie Arbeit an konkreten physikalischen Aufgaben in Kleingruppen im PC-Pool unter Anleitung statt. Im Beitrag werden die organisatorisch-technische Umsetzung sowie die gewonnenen Erkenntnisse aus dieser Veranstaltungsform präsentiert.
Literaturhinweise
Lage, M. J., Platt, G. J., & Treglia, M. (2000). Inverting the classroom: A gateway to creating an inclusive learning environment. The Journal of Economic Education, 3 (1), 30 - 43,
https://doi.org/10.2307/1183338
J. Handke, A. Sperl (Hrsg.): Das Inverted Classroom Model. Oldenbourg, München 2012, ISBN 978-3-486-71652-8.
A. Sauter, W. Sauter: Blended Learning. Effiziente Integration von E-Learning und Präsenztraining. Luchterhand, Neuwied 2004, ISBN 3-472-05592-8.
https://www.ecademy-learning.com/ausbildung-digital/blended-learning/
Python: https://www.python.org/
Jupyter Notebook: https://jupyter.org/
Jupyterhub: https://jupyter.org/hub
OPAL LTI: https://www.bps-system.de/help/display/LMS/LTI-Tool
Gitlab: https://gitlab.mn.tu-dresden.de/
nbmerge: https://github.com/jbn/nbmerge
nbgitpuller: https://github.com/jupyterhub/nbgitpuller
Angaben zum Artikel
| DOI | |
|---|---|
| Veröffentlicht |
Dezember 28, 2022
|
| Ausgabe | |
| Rubrik |
Artikel
|
| Schlagworte | python, jupyter notebooks |
| Zitationsvorschlag |
Brose, J. (2022). Blended Learning mit Jupyter Notebooks. Lessons Learned, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.25369/ll.v2i2.52
|
| Lizenz |
Copyright (c) 2022 Jens Brose  Dieses Werk steht unter der Lizenz Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International. |